Power
Digital power grids as a basis for energy efficiency
Generation, transmission, distribution and electricity marketing companies provide a highly critical service with strict quality requirements in an increasingly complex technological environment in order to control and manage the energy system and its costs.
We offer customers in the power sector the most advanced solutions based on our strong knowledge of business processes and our technological capacity contrasted with the most important agents in the sector.
In order to solve the requirements of digital power networks, we cover the main objectives of the electrical system.
Practical solutions in the control of each process
Implemental Systems offers high value solutions and services that make us the best strategic partner to meet the current and future challenges and opportunities of the power sector.
Digital power networks
The solutions prepared for the electricity sector enable two-way communication between the company and its customers and the intelligent management of the electricity transmission and distribution network in order to adapt power companies to the international principles of smart grid: to incorporate information and communications technology in all aspects of electricity generation, supply and consumption in order to minimise environmental impact, improve markets, improve reliability and service, and reduce costs and improve efficiency.
Transmission
Solutions that allow to manage and monitor transmission assets allowing an optimization of both technical and human resources.
Implemental Systems offers integral solutions implementing the different components of architecture that automate the operational business processes.
EMS-SCADA
Transmission Business Intelligence
Transmission OMS
Network Design Planning
Asset Management and Inventory
Mobility Management
-
EMS-SCADA
Energy Management System is a modular solution that provides advanced applications specifically designed to monitor, analyze, optimize, simulate and centrally control the network of generation, transmission and distribution of geographically dispersed assets of a power utility in real time.
-
Transmission Business Intelligence
Allows easy and efficient access to data from different spatial and non-spatial systems of the transmission network. This data can be shared across the enterprise to empower a wide range of users with viewing, querying, analyzing and reporting.
-
Transmission OMS
Information system aimed at minimising the impact of power outages on the transmission network, based on network inventory and circuit connectivity.
-
Network Design Planning
Plan new networks or renew existing segments of the transmission network. This is achieved with projects through a workflow management system and version management.
-
Asset Management and Inventory
Allows the recording and management of the life cycle of the fixed inventory elements of the transmission network. It includes information about the physical and intangible properties of the element, as well as its geographical location and its connection with other elements.
-
Mobility Management
Allows the management and monitoring of field actions derived from preventive or corrective maintenance operational processes for transmission network elements.
Distribution
Distribution
In the field of power distribution, we configure the most advanced technological solutions implemented worldwide, which allow the distribution network to operate efficiently.
-
ADMS-SCADA
A single user interface environment, fully integrated, with intuitive and advanced navigation, designed for daily operational management of the power grid to control load flows, demand estimates, countermeasures in the event of faults and power outages.
-
Distribution OMS
Includes trouble call management, customer notification, prediction of failing devices, workflows for outages and general power problems, network management, crew management and reliability reports.
-
Distribution Business Intelligence
Allows easy and efficient access to data from different spatial and non-spatial-based systems in the distribution network. This data can be shared across the enterprise to empower a wide range of users with visualization, query, analysis and reporting.
-
Network Design Planning
Plan new networks or renew existing segments of the distribution network. This is achieved with projects through a workflow management system and version management.
-
Asset Management and Inventory
Allows the recording and management of the life cycle of the fixed inventory elements of the transmission network. It includes information about the physical and intangible properties of the element, as well as its geographical location and its connection with other elements.
-
Mobility Management
Supports call logging, service reservation, resource planning, automation of the work lifecycle process, operations dashboard, automated crew deployment, activity logging, used parts and cost monitoring, SLA tracking, risk management, route calculation and visualization.
-
Preventive Construction and Maintenance
Allows the management of preventive maintenance of network resources according to the life cycle of the elements according to the specifications made by the manufacturer and the date of installation, as well as the updating of modified elements or spare parts.
ADMS-SCADA
Distribution OMS
Distribution Business Intelligence
Network Design Planning
Asset Management and Inventory
Mobility Management
Preventive Construction and Maintenance
Consumption Management
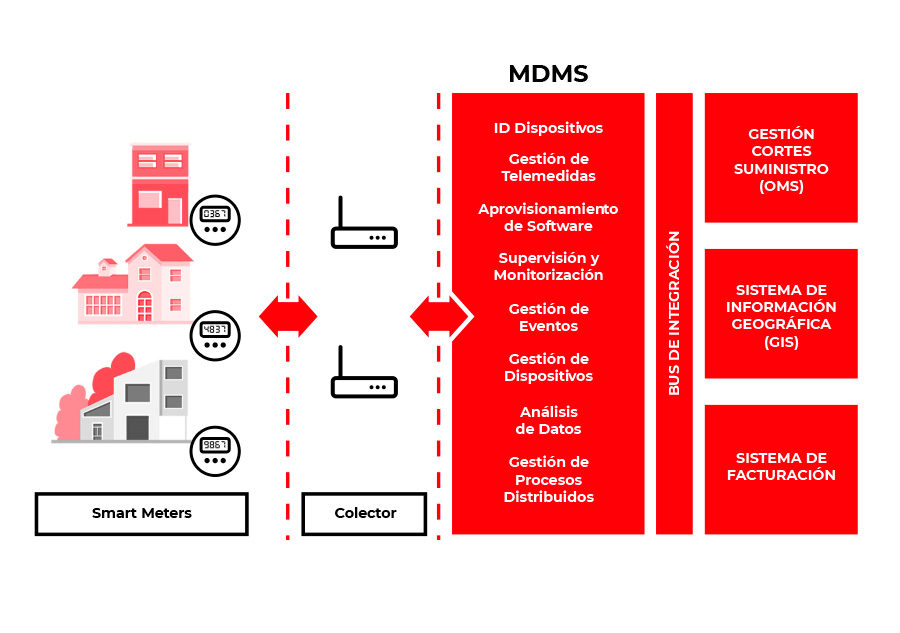
It is achieved through the supervision of Smart Meters, which are electronic metering devices used by utilities to communicate billing information and the status of supply operations.
The use of these smart meters with bidirectional means of information communication, monitoring and control is the basis for an Advanced Metering Infrastructure or AMI.
The general structure of the meters maintains the three main elements of a meter such as the measurement system, the memory and the main information device that is now the communications system.

-
Meter monitoring
The AMI makes it possible to monitor the status and measurements taken by smart meters.
-
Transformer Monitoring
The SCADA elements installed in the transformation centers transmit information in real time to the back office such as voltage or intensity.
-
Outage monitoring
The OMS transforms SCADA alerts into power outages and tracks them until the service is restored.
Telemetry
The Meter Data Management system provides the necessary database and tools for managing the data collected on the network and makes them available to the company.
-
Smart Meters
These are the devices installed at the access point to the network of each customer and continuously monitor its electricity consumption.
-
Collectors
They are organized into local networks, each of which has a concentrator terminal associated with it that acts as a coordinating node for the network. Its main function is to serve as a communications gateway between the local network and the backbone communications network that will transmit information to the central information systems of the power utility.
-
MDMS
It contains many modules with defined functionalities such as measurement device management, telemetry operations, software provisioning, distributed process management, supervision and monitoring, data analysis, alarm management, device identification.
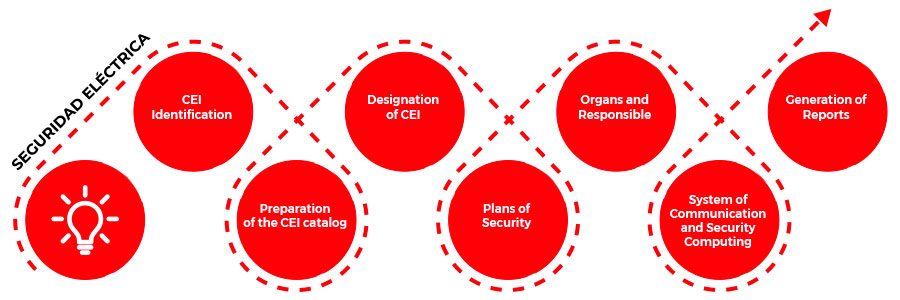
Digital Power System Security
The protection of critical energy infrastructure (CEI) is a concern of developed states. Guaranteeing the security of energy supplies in the face of the new threats of the new century is not only the responsibility of public administrations, but also requires the awareness and collaboration of private operators.
Implemental Systems contributes to this objective with the following services:
- Identification of CEI.
- Elaboration of the CEI Catalogue.
- Designation of CEI: to define the communication protocol and the requirements for the owner or operator of CEI
- Operator security plans. Specific Protection Plans for each Infrastructure.
- Identification of relevant elements.
- Analysis of risks and vulnerabilities.
- Selection of controls (specifying identification, selection and priority of safeguards).
- Communication protocols between the Operator and the Administration.
- Security Organs and Officers. Definition of the different roles and responsibilities involved in the protection of CEI, both public and private sector agents.
- Communication Systems and Information Security. Recommendations for the establishment of a secure information and communication system that guarantees the confidentiality and protection of CEI-related data.
- Generation of reports. preparation of the necessary control system for monitoring the protection plans, by defining the reports to be generated by the operators or owners of the CEI.